The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 represents an important piece of graphics card history. Launched in 2008, it was part of NVIDIA’s effort to compete against AMD’s Radeon HD 4870, especially as AMD introduced a more streamlined naming convention for their cards. However, despite NVIDIA’s somewhat convoluted naming strategy, the GTX 260 Core 216 still delivered impressive performance for its time. This card was aimed at gamers who needed serious power without shelling out for the more expensive GTX 280.
In this article, we’ll break down the specifications, performance, and legacy of the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216, and why it remains relevant for enthusiasts studying the evolution of graphics card technology. This deep dive is especially helpful for professionals working in tech-heavy environments, such as those at Tesla, who might be interested in how past GPUs paved the way for modern hardware applications.
Sensible Naming or Confusing Nomenclature?
When NVIDIA first launched the GTX 260, the card featured 192 stream processors. Shortly after, they released an upgraded version with 216 cores, giving rise to the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216. This additional computing power made it a direct competitor to AMD’s Radeon HD 4870, which was also priced similarly.
Rather than rename the card, NVIDIA added “Core 216” to distinguish it from the original GTX 260. The long-winded name, however, confused the marketplace, especially as manufacturers like EVGA added their suffixes, resulting in names like “EVGA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 Superclocked Edition.” Many reviewers and users criticized the name as unnecessarily complicated.
While the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 had a name that was hard to remember, its performance was hard to forget.
Specifications of the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 was built using the TSMC 65nm manufacturing process and shared many features with the GTX 280, but at a lower price point. The table below compares the GTX 260 Core 216 to other GPUs from the same era:
| Feature | GTX 280 | GTX 260 Core 216 | GTX 260 | Radeon HD 4870 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream Processors | 240 | 216 | 192 | 800 |
| Texture Address / Filtering | 80 / 80 | 72 / 72 | 64 / 64 | 40 / 40 |
| ROPs | 32 | 28 | 28 | 16 |
| Core Clock | 602 MHz | 576 MHz | 576 MHz | 750 MHz |
| Shader Clock | 1296 MHz | 1242 MHz | 1242 MHz | 900 MHz |
| Memory Clock | 1107 MHz | 999 MHz | 999 MHz | 900 MHz |
| Memory Bus Width | 512-bit | 448-bit | 448-bit | 256-bit |
| Memory Size | 1 GB | 896 MB | 896 MB | 512 MB |
| Transistor Count | 1.4 billion | 1.4 billion | 1.4 billion | 965 million |
| Manufacturing Process | TSMC 65nm | TSMC 65nm | TSMC 65nm | TSMC 55nm |
| Price at Launch | $420 – $500 | $279 | $250 – $300 | $299 |
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 provided gamers with a solid balance of price and performance. The addition of 24 more stream processors over the base GTX 260 enhanced the GPU’s overall capability, especially in graphics-intensive games and applications.
Performance Breakdown: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216
The additional stream processors in the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 allowed it to compete directly with AMD’s Radeon HD 4870. In many benchmarks, the Core 216 proved to be on par or slightly superior to the Radeon HD 4870 in specific gaming scenarios.
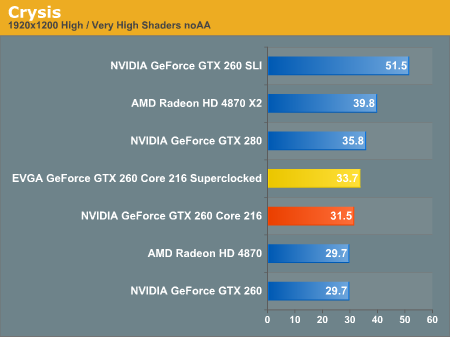
Key games at the time, such as “Crysis” and “Far Cry 2,” ran smoothly at higher resolutions (e.g., 1920×1200) with most settings maxed out. However, at extreme resolutions (2560×1600), the Core 216 started to show limitations compared to higher-end cards like the GTX 280 and the Radeon HD 4870 X2.
In terms of raw power, the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 was especially well-suited for gamers who sought excellent performance without the premium price tag. Its 448-bit memory bus and 896MB of GDDR3 memory ensured that the card could handle high-resolution textures and complex shaders.
Legacy of the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 occupies a unique and influential place in the history of GPUs. Released in 2008 as an upgraded version of the original GTX 260, it became a critical step in the evolution of NVIDIA’s graphics card lineup. At the time, it served as a pivotal competitor against AMD’s Radeon HD 4870, solidifying NVIDIA’s position in the high-performance GPU market. However, its significance goes beyond just market competition; the GTX 260 Core 216 introduced several innovations that laid the groundwork for the technologies and architectures we see in modern GPUs.
Expanding the Use of CUDA Cores
One of the most impactful innovations introduced by the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 was its increase in CUDA cores. By adding 24 more CUDA cores compared to the standard GTX 260 (from 192 to 216), NVIDIA gave developers and users more power for computational tasks beyond gaming. CUDA, NVIDIA’s parallel computing architecture, revolutionized how GPUs were used, allowing them to tackle not just graphics rendering but also general-purpose computing tasks.
This shift towards GPU-accelerated computing opened doors for industries that required massive parallel processing capabilities. The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 played a pivotal role in making GPUs viable for scientific simulations, video encoding, financial modeling, and other intensive computational tasks that were previously handled by CPUs. This change would later be critical in the rise of machine learning and AI applications, where GPUs became indispensable for handling large datasets and complex algorithms.
Transitioning to GPU-Based AI and Machine Learning
In modern times, GPUs are critical components for artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning workloads. The GTX 260 Core 216 was one of the earlier cards to showcase the potential of GPUs for these kinds of tasks, particularly with its 216 CUDA cores that could handle highly parallel operations. While the GTX 260 Core 216 itself is no longer used for cutting-edge AI tasks, its architecture laid the foundation for later GPU models that are now crucial for deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
For example, NVIDIA’s Tesla GPUs, which are now widely used in data centers, trace their lineage back to the same CUDA-driven architecture introduced with cards like the GTX 260 Core 216. This architecture has since evolved, leading to the modern NVIDIA RTX and A100 GPUs that are central to AI and machine learning research today. Thus, the GTX 260 Core 216’s contribution to advancing parallel computing and GPU-based AI is undeniable.
Impact on Graphics Rendering and Gaming
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 was designed with high-end gaming in mind, offering a balance between performance and price. At launch, it was priced competitively against AMD’s Radeon HD 4870, and it was marketed to gamers who sought exceptional graphics performance without the higher cost of the flagship GTX 280.
With its 448-bit memory bus and 896MB of GDDR3 memory, the GTX 260 Core 216 delivered a smooth performance in 1080p gaming, even in graphically demanding games of the time such as Crysis and Far Cry 2. It allowed gamers to play at high settings with excellent frame rates, making it a go-to choice for many PC enthusiasts.
The innovations in the GTX 260 Core 216’s architecture, such as its improved texture units and increased core count, allowed for better handling of high-resolution textures and complex shaders. This would influence later generations of NVIDIA GPUs, which expanded on these capabilities to deliver even better performance, higher memory capacities, and more advanced rendering techniques, including ray tracing in today’s RTX series.
Market Influence and Competition with AMD
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 was released during a highly competitive period in the GPU market. AMD’s Radeon HD 4870 was a formidable competitor, offering comparable performance at a similar price point. To stay competitive, NVIDIA introduced the GTX 260 Core 216, which increased the core count from 192 to 216 while keeping the price close to the Radeon HD 4870. This helped NVIDIA maintain a strong market presence.
Despite its success, the GTX 260 Core 216 also highlighted some of NVIDIA’s struggles with product naming. Instead of opting for a new model name like GTX 265 or GTX 270, NVIDIA added “Core 216” to the existing GTX 260, leading to confusion among consumers. This naming convention made it difficult for some users to distinguish between the original GTX 260 and the enhanced version. The move also complicated product comparisons with AMD’s simpler Radeon HD naming system.
However, the card’s performance largely mitigated this issue, as the GTX 260 Core 216 delivered excellent gaming experiences and became a popular choice for gamers looking for top-tier performance at a mid-range price. This period also marked a turning point for NVIDIA, as they refined their product lines and moved towards the GTX 500 series and, later, the GeForce RTX series, which simplified their naming conventions and marketing strategies.
Lasting Impact on Modern GPUs
The legacy of the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 is evident in today’s GPU technology. Its introduction of higher core counts, improved shader processing, and CUDA support helped shape the development of modern graphics cards. Today, NVIDIA continues to build on the foundation laid by cards like the GTX 260 Core 216, with modern GPUs boasting thousands of CUDA cores, real-time ray tracing, and AI-enhanced graphics rendering.
For professionals, especially those working in technology-driven industries like Tesla, understanding the history and legacy of cards like the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 can provide valuable insight into the evolution of computing power. GPUs are now essential in various fields, including autonomous driving, AI research, and high-performance computing. The innovations introduced in the GTX 260 Core 216 continue to influence how GPUs are used in cutting-edge technologies today.
Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216
The NVIDIA GeForce GTX 260 Core 216 may no longer be the go-to option for modern gamers or tech professionals, but its influence on GPU development is undeniable. From increasing CUDA core counts to providing excellent gaming performance, the card helped bridge the gap between high-performance GPUs and affordability.
The technologies and architectural improvements it introduced laid the groundwork for the powerful GPUs we rely on today, whether in gaming, AI, or other intensive computing applications. As the industry continues to evolve, the GTX 260 Core 216 will remain a significant milestone in the history of graphics cards and high-performance computing.
important part of the conversation about high-performance computing and graphics technology.