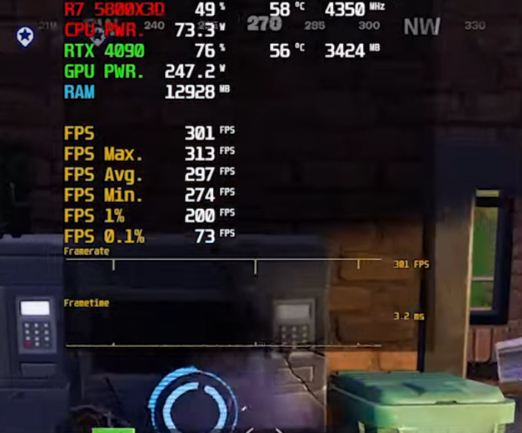
When building or upgrading a gaming or productivity-focused PC, choosing the right CPU is crucial. Two of AMD’s standout processors—the Ryzen 7 5800X3D and Ryzen 7 7800X3D—are often compared due to their 3D V-Cache technology, making them particularly strong choices for gamers. But while both deliver excellent performance, they cater to different types of users depending on factors such as budget, future-proofing, and overall system goals.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the 5800X3D vs 7800X3D comparison, analyzing their architectural differences, gaming performance, productivity benchmarks, thermals, power efficiency, and price-to-performance ratios to help you make an informed decision.
Overview of AMD’s 3D V-Cache Technology
Both the 5800X3D and 7800X3D processors benefit from AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology, a breakthrough in chip design. This technology allows additional L3 cache to be stacked vertically on top of the CPU die, significantly increasing the amount of cache available to the processor. This extra cache is particularly useful for workloads that benefit from quick data access, such as gaming and some computational tasks.
By increasing the L3 cache to 96MB, these processors can reduce latency and improve performance in games that rely heavily on the CPU. This technology marks a significant leap over AMD’s traditional Ryzen chips, especially for users who seek top-tier gaming performance.
Architectural Differences: Zen 3 vs Zen 4
The 5800X3D is based on AMD’s Zen 3 architecture, while the 7800X3D utilizes the more advanced Zen 4 architecture. These differences in architecture are key to understanding the performance gaps between the two chips.
- 5800X3D (Zen 3): Released as part of AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series, this CPU is an 8-core, 16-thread processor with base and boost clock speeds of 3.4 GHz and 4.5 GHz, respectively. Despite being based on the 7nm manufacturing process, the 5800X3D introduces 3D V-Cache, giving it a significant performance boost in gaming scenarios over the standard 5800X.
- 7800X3D (Zen 4): Launched with AMD’s Ryzen 7000 series, the 7800X3D also features 8 cores and 16 threads but benefits from architectural improvements inherent to the Zen 4 architecture. These improvements include a 5nm manufacturing process, higher base and boost clocks at 4.2 GHz and 5.0 GHz, and full support for PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 memory.
The architectural changes in Zen 4 result in better performance across the board. Even though both chips share the same 3D V-Cache, the 7800X3D benefits from higher clock speeds, greater power efficiency, and improved memory bandwidth, particularly when paired with DDR5 RAM.
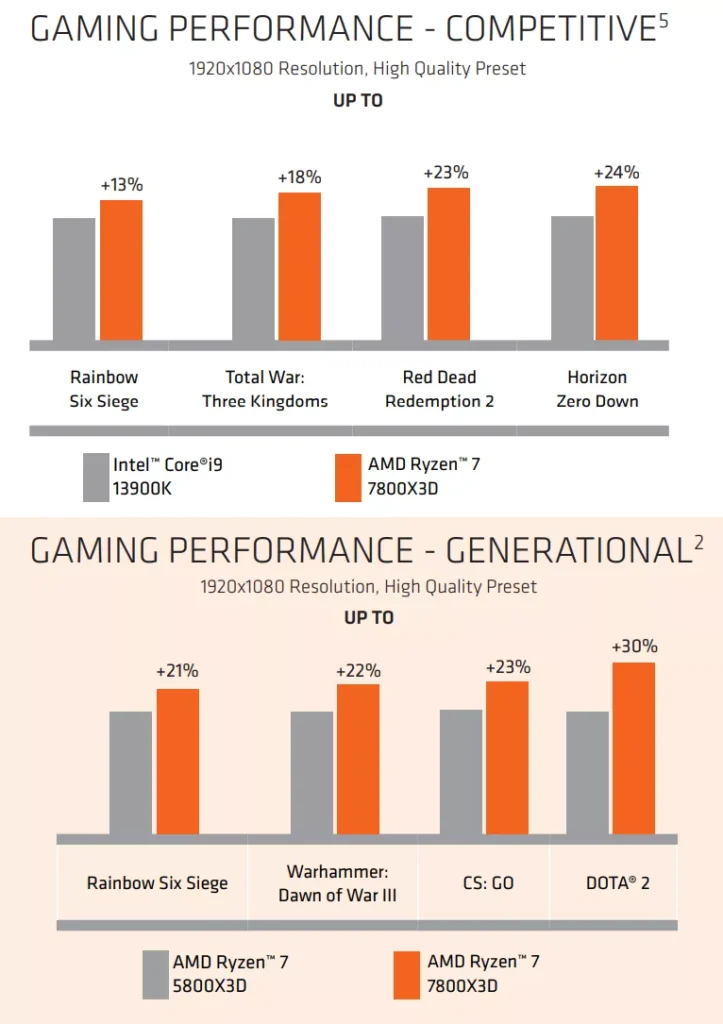
Gaming Performance
For gamers, the 5800X3D vs 7800X3D debate is crucial, as both processors are specifically tuned for gaming performance due to their large caches. However, the question remains: which one should you choose for gaming?
5800X3D Gaming Performance
The 5800X3D quickly gained a reputation as one of the best gaming CPUs upon its release, largely due to the increased L3 cache. The large cache significantly reduces latency, providing smoother performance in CPU-heavy games like Shadow of the Tomb Raider, Cyberpunk 2077, and Assassin’s Creed Valhalla.
In terms of raw gaming power, the 5800X3D outperforms many of its Zen 3 counterparts and even competes with some of Intel’s 12th-gen CPUs. However, it is somewhat limited by its reliance on DDR4 memory and PCIe 4.0, which can bottleneck performance in the most demanding next-gen games when paired with the latest GPUs, such as the NVIDIA RTX 4080 or AMD RX 7900 XTX.
7800X3D Gaming Performance
The 7800X3D takes gaming performance to the next level by combining the benefits of 3D V-Cache with the generational improvements of the Zen 4 architecture. With its faster clock speeds, DDR5 memory support, and PCIe 5.0, it offers superior performance in gaming, especially in titles that rely heavily on CPU performance or memory bandwidth.
In benchmark comparisons, the 7800X3D outperforms the 5800X3D by 10-15% in modern AAA titles, particularly at higher resolutions like 1440p and 4K. This makes it the better choice for gamers who are building a new system and want to future-proof their setup for several years to come.
Productivity and Content Creation
While both processors excel in gaming, it’s also important to consider their performance in productivity tasks, such as video editing, 3D rendering, and multitasking. Here’s how they compare in these areas:
5800X3D Productivity Performance
The 5800X3D is no slouch when it comes to content creation, but it’s primarily designed with gaming in mind. In workloads like video rendering or Blender benchmarks, the 5800X3D performs well, but its lower clock speeds and DDR4 memory support limit its potential compared to newer models. For users primarily focused on gaming with occasional productivity work, the 5800X3D is still a strong contender.
7800X3D Productivity Performance
Thanks to the Zen 4 architecture, the 7800X3D shines in productivity tasks. Its higher clock speeds, support for DDR5 memory, and improvements in core efficiency make it significantly faster in multithreaded workloads compared to the 5800X3D. In benchmarks like Cinebench R23 or Adobe Premiere Pro, the 7800X3D consistently outperforms the 5800X3D, delivering faster rendering times and better multitasking capabilities.
If you’re a content creator or someone who frequently engages in 3D rendering or video editing, the 7800X3D is the better choice, offering superior performance in both gaming and productivity tasks.
Power Efficiency and Thermals
The 5800X3D and 7800X3D differ in terms of power efficiency and thermal performance, largely due to their respective architectures.
- 5800X3D: Built on a 7nm process, the 5800X3D is efficient compared to earlier AMD CPUs but consumes more power than its Zen 4 counterparts. Under load, it can reach higher temperatures, especially during sustained gaming or productivity sessions. If you choose the 5800X3D, it’s recommended to pair it with a quality cooling solution to maintain stable performance.
- 7800X3D: Thanks to its 5nm process and Zen 4 architecture, the 7800X3D is more power-efficient and runs cooler, even at higher clock speeds. This makes it an ideal choice for users looking to build energy-efficient PCs that don’t sacrifice performance. Additionally, its efficiency makes it more suitable for overclocking, giving users more headroom to push the chip to its limits without significantly increasing temperatures or power draw.
DDR5 vs DDR4: Memory Support
One of the most important differences between these processors is memory support:
- 5800X3D: Limited to DDR4 memory, the 5800X3D is still able to provide excellent performance in most gaming and productivity scenarios. However, DDR4 is beginning to show its age, especially in bandwidth-intensive tasks like video editing or high-end gaming.
- 7800X3D: Supports DDR5 memory, which offers increased bandwidth, lower latency, and higher overall performance. In gaming, the performance gap between DDR4 and DDR5 may be small for now, but as more software and games are optimized for DDR5, the 7800X3D’s support for this next-gen memory standard gives it a significant advantage.
PCIe 5.0 vs PCIe 4.0: Future-Proofing
Another key difference between the 5800X3D and 7800X3D is PCIe support:
- 5800X3D: Limited to PCIe 4.0, the 5800X3D can still deliver excellent performance when paired with the latest NVIDIA or AMD GPUs, but as PCIe 5.0 becomes more widely adopted, the 5800X3D may fall behind in terms of compatibility with future hardware.
- 7800X3D: Supports PCIe 5.0, which not only benefits next-gen GPUs but also allows for faster NVMe SSDs that can take advantage of the increased bandwidth. If you’re building a new system with an eye toward future upgrades, PCIe 5.0 ensures that your 7800X3D build will remain compatible with emerging hardware for several years.
Motherboard Compatibility and Upgrade Path
Another essential consideration in the 5800X3D vs 7800X3D debate is their compatibility with different platforms, which significantly impacts their upgrade potential.
- 5800X3D: This processor is part of the AM4 platform, which has been around for several years and offers compatibility with a wide range of motherboards. For users upgrading from an older Ryzen CPU, the 5800X3D allows for an easy drop-in upgrade without needing to replace the motherboard, memory, or other components. However, since AMD has moved to the AM5 socket with its latest CPUs, the AM4 platform is nearing the end of its lifecycle. While the 5800X3D can still provide several years of excellent performance, it does not have access to PCIe 5.0 or DDR5 support, which means its upgradability is more limited compared to newer platforms.
- 7800X3D: Built on the AM5 platform, the 7800X3D is a more future-proof option. AM5 supports both DDR5 memory and PCIe 5.0, giving you access to next-gen technologies and greater future upgradability. The AM5 platform is expected to be supported by AMD for several years, making it a solid investment for those who want their system to remain relevant as newer hardware becomes available. Additionally, AM5 motherboards offer improved connectivity options and features like USB 4.0, faster NVMe storage, and better support for high-speed memory overclocking.
Upgrade Costs and Platform Longevity
The overall cost of upgrading or building a system around either the 5800X3D or 7800X3D varies significantly based on platform considerations.
- 5800X3D: For users with an existing AM4 system, upgrading to the 5800X3D is highly cost-effective. Since it uses DDR4 and PCIe 4.0, most users won’t need to upgrade additional components like RAM or their motherboard. This makes the 5800X3D an ideal choice for gamers looking to squeeze more performance out of their existing systems without breaking the bank.
- 7800X3D: For those building a new system, the 7800X3D will likely involve higher upfront costs. Not only is the processor itself more expensive, but the AM5 motherboard and DDR5 RAM required to build around this CPU also come at a premium. However, these additional costs can be justified by the future-proof nature of the platform, ensuring compatibility with the latest technologies for years to come. This makes the 7800X3D a better investment for users who plan to upgrade their system incrementally over time without needing to switch platforms again in the near future.
Overclocking Capabilities
Both the 5800X3D and 7800X3D processors feature a 3D V-Cache, which makes them less ideal for traditional overclocking compared to other Ryzen CPUs. However, there are still some differences in how these two chips handle performance tweaks.
- 5800X3D: Due to the thermal limitations introduced by the 3D V-Cache, the overclocking potential on the 5800X3D is limited. Most users will find that manually pushing the clock speeds higher doesn’t yield significant performance improvements, and the chip performs best with factory-set clock speeds. That said, advanced users may still explore undervolting options to improve thermals or boost performance through memory overclocking with DDR4.
- 7800X3D: The 7800X3D benefits from the improvements in Zen 4 architecture, offering better power efficiency and thermal performance. Although 3D V-Cache still limits aggressive overclocking, the higher base and boost clocks, combined with DDR5 memory, allow for improved performance tuning. Additionally, AM5 motherboards tend to offer more robust overclocking tools, making it easier for users to experiment with memory overclocking or fine-tuning power settings for better overall efficiency.
Real-World Usage and User Experience
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing between the 5800X3D and 7800X3D is how each processor performs in real-world usage, not just synthetic benchmarks.
- 5800X3D: For users upgrading from older Ryzen processors or those on a budget, the 5800X3D provides an incredibly smooth and reliable experience in both gaming and general productivity. It remains one of the best value CPUs for high-end gaming, especially for those sticking with DDR4 systems. The slightly lower thermal performance and limited upgrade path make it less ideal for users looking to push their systems to the bleeding edge.
- 7800X3D: With Zen 4’s improvements in clock speeds, memory support, and power efficiency, the 7800X3D offers a more future-proof experience for gamers and content creators alike. For those building new systems, the AM5 platform ensures compatibility with the latest technologies, and the improved architecture allows for better performance across the board, whether you’re gaming, rendering, or multitasking.
Conclusion: Which CPU is Right for You?
In the 5800X3D vs 7800X3D comparison, both processors excel in different areas, making the choice highly dependent on your specific needs.
- 5800X3D: Ideal for gamers looking for a budget-friendly upgrade to their existing AM4 system. Its 3D V-Cache ensures top-tier gaming performance, and the cost savings of staying on DDR4 and PCIe 4.0 make it one of the best value options for gaming enthusiasts who want excellent performance without breaking the bank.
- 7800X3D: The better choice for those building a new system or looking to future-proof their setup. The Zen 4 architecture, DDR5 memory support, and PCIe 5.0 compatibility make the 7800X3D the superior choice for long-term performance, especially in productivity tasks and CPU-bound gaming scenarios. While it comes with a higher price tag and platform cost, the 7800X3D offers significant performance improvements and access to the latest technologies.
Ultimately, your decision should be based on your budget, the hardware you already own, and how important future-proofing is for your build. Both CPUs are excellent options, but the 7800X3D edges ahead with its modern platform and next-gen support.